Published 5/2024
Created by Hemakumar Kasala
MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: AAC, 44.1 KHz, 2 Ch
Genre: eLearning | Language: English | Duration: 5 Lectures ( 1h 41m ) | Size: 789 MB
Essential statistics for data science
What you'll learn:
Learn all about sampling in statistical studies. Bias and different possible types of bias during sampling. Representative samples and various sampling methods
Sampling to estimate the population mean. Sample mean probability distribution. Mean & variance in the sample mean distribution. And central limiting theorem.
Sampling to estimate the population proportion of success. Sample proportion probability distribution. Mean & variance in sample proportion distribution
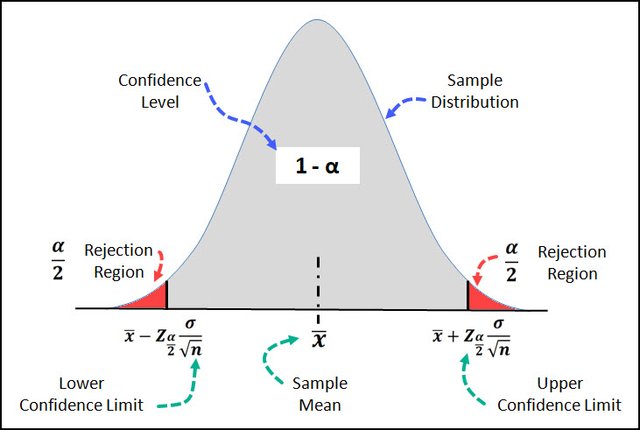
Single sample Point estimate / sample statistic. Confidence interval and confidence levels. Estimating the z statistic and t-statistic and z/t statistic tables
Requirements:
A fair knowledge on Random variables and probability distributions should help understand this course better and faster. I have published a separate course on this topic that the student may go throughon this topic
Description:
Statistical studies are often about understanding, estimating various population characteristics.Since it is often not feasible to undertake the study on the entire population the statistical study is often carried out on a representative sample drawn out of the populationTherefore the said sample has to meet certain expectations in order to be a fairly good representative of the population.This course starts with the topic that explain the factors to be understood and implemented as part of the sampling processFrom the sample a sample statistic representing a population characteristic of interest is derived. Population characteristic of interest is often one among the following two {Population proportion of success, Population mean}A sample statistic is a single sample point estimate of the population characteristic. Therefore the sample statistic exhibits a probability distribution as sampling and sample statistic are derived repeatedly over large number of cycles. This course explains the characteristics of such a sample statistic distribution for both kinds of sample statistics namely { Sample proportion of success, Sample mean}. Explains the mean and standard deviations for these distributions and how they are related to population characteristics and sampling sizes.The course further explains how to use the sample statistic (single sample Point estimate) to get an idea of the population characteristic using an additional estimate called as the confidence interval. Point estimate and confidence interval together identify the interval that captures the true unknown population characteristic.The course also explains how to apply the Z standard normal statistic , t-statistic and their respective Z/T statistic tables in the above process to arrive at the estimates for the population characteristics.
Who this course is for:
This course a one part of the essential statistics that every data science / machine learning aspirants should know about. However statistics as such is applied widely across many disciplines namely management, medical , economics etc.
Homepage
https://k2s.cc/file/ece9cbf4ab7a7 https://rapidgator.net/file/5056f80b636e8a32b0725f9a967e240e/Sampling_distributions,_point_estimate_&_confidence_interval.rar.html

 Help
Help











